Transesophageal Echocardiography
What is Transesophageal Echocardiography?
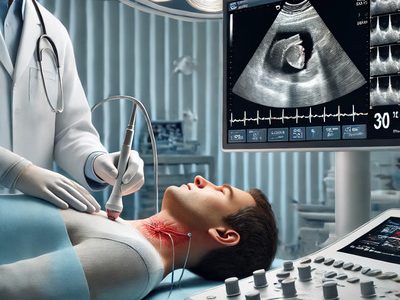
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) provides detailed images of the heart when traditional echocardiography is not sufficient. This procedure involves several steps to ensure comfort and accuracy for the patient.
Procedure Overview:
- Preparation: First, we administer medication to numb the throat and a sedative to help the patient relax and not remember the procedure.
- Insertion of the Probe: A specialized ultrasound probe is carefully inserted through the patient’s mouth and into the esophagus. This position provides clear images of the heart, which is located directly behind the esophagus.
- Imaging: The probe emits sound waves, which bounce back to create high-resolution, real-time images of the heart. TEE helps assess heart valve function, chamber size, and detect clots or infections, especially in cases of atrial fibrillation or endocarditis.
- Procedure Duration: The procedure typically lasts 10 to 15 minutes.
- Recovery: Afterward, the patient rests as the sedation wears off, typically recovering within 30 minutes to an hour. Since the procedure involves sedation, the patient will need someone to assist them with transportation home.
Advantages of Transesophageal Echocardiography:
- Superior Imaging: TEE provides clearer, more detailed images than standard echocardiography, especially for areas of the heart difficult to view from the chest.
- Non-Invasive: TEE is a non-surgical procedure that offers crucial diagnostic information with minimal discomfort.
- Helpful in Complex Cases: TEE is often used to assess valvular heart disease, endocarditis, stroke, or blood clots, providing higher diagnostic accuracy.
Common Indications for Transesophageal Echocardiography:
- Heart Valve Assessment: To evaluate valve function, especially in mitral valve disease or endocarditis cases.
- Detection of Blood Clots: To identify clots in the heart, particularly in patients with atrial fibrillation.
- Aortic Abnormalities: To assess conditions like aortic dissection or aneurysms.
- Prosthetic Valve Evaluation: For monitoring patients with heart valve replacements or repairs.
- Endocarditis: To detect infections in the heart lining or valves.
